In this informative article, we will explore the undeniable connection between hypertension and heart disease. As we delve into the depths of this topic, you will gain a better understanding of the link between these two health conditions. With hypertension, or high blood pressure, affecting millions worldwide, it becomes crucial to grasp the potential dangers it poses to our heart health. Join us on this journey as we embark on unraveling the intricacies of this vital connection and uncover ways to protect our hearts from the consequences of hypertension.
This image is property of pixabay.com.
Check out our Product Reviews
Defining Hypertension
Hypertension, commonly known as high blood pressure, is a medical condition in which the force of blood against the walls of your arteries is consistently too high. Blood pressure is measured using two numbers: systolic pressure (the pressure when the heart beats) and diastolic pressure (the pressure when the heart is at rest between beats). A normal blood pressure reading is typically around 120/80 mmHg. However, if your blood pressure consistently measures above 130/80 mmHg, you may be diagnosed with hypertension.
The Prevalence of Hypertension
Hypertension is a global health issue that affects millions of people worldwide. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), hypertension is estimated to affect around 1.13 billion people, accounting for approximately 1 in 4 adults globally. This prevalence is expected to increase in the coming years due to various risk factors and lifestyle changes.
Several risk factors contribute to the development of hypertension, including age, family history, unhealthy diet, sedentary lifestyle, tobacco use, excessive alcohol consumption, and obesity. These factors, coupled with the increasing incidence of chronic diseases such as diabetes and kidney disease, make hypertension a significant public health concern.
Check out our Product Reviews
Hypertension and Cardiovascular Disease
Hypertension is closely linked to cardiovascular disease, which refers to conditions that involve the heart and blood vessels. Heart disease and hypertension often coexist, with one condition exacerbating the other. When blood pressure is consistently high, the heart has to work harder to pump blood throughout the body. This increased workload can lead to various cardiovascular issues.
Coronary artery disease (CAD), a common form of heart disease, occurs when the arteries that supply blood to the heart muscle become narrowed or blocked due to a buildup of plaque. Hypertension can accelerate the progression of CAD by damaging the arterial walls and promoting the formation of plaques. As a result, individuals with hypertension are at a higher risk of experiencing a heart attack or myocardial infarction.
Mechanisms behind the Link
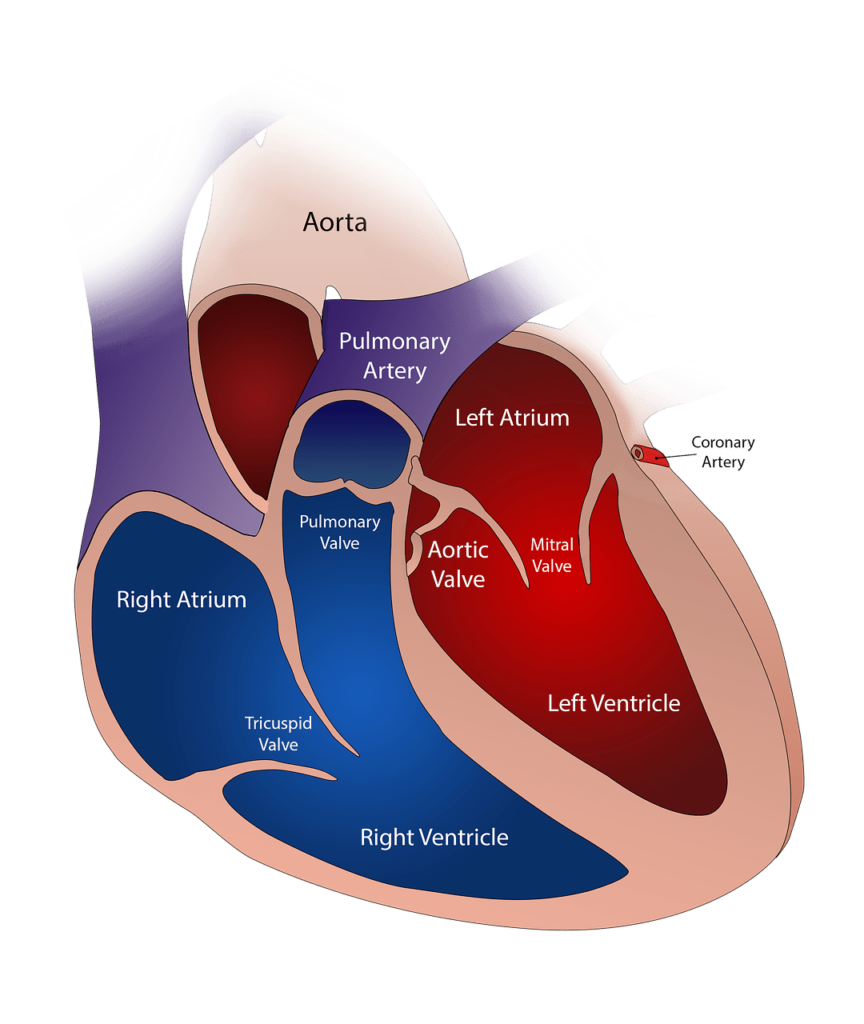
The connection between hypertension and heart disease can be attributed to several mechanisms. Firstly, high blood pressure puts constant strain on the arteries, making them less elastic and more prone to damage. Over time, this can lead to the development of atherosclerosis, a condition characterized by the formation of fatty plaques in the walls of the arteries.
Additionally, hypertension can cause structural changes in the heart itself. The increased workload on the heart muscles can lead to the thickening of the heart walls, a condition known as left ventricular hypertrophy. This thickening reduces the heart’s ability to pump effectively and increases the risk of heart failure.
This image is property of pixabay.com.
Complications of Hypertension
If left untreated, hypertension can have severe consequences on various organs and increase the risk of developing life-threatening conditions. One of the most concerning complications is an increased risk of stroke. High blood pressure damages the blood vessels in the brain, making them more susceptible to rupture or blockage, resulting in a stroke.
Hypertension also poses a significant risk to the kidneys. The kidneys are responsible for filtering waste and excess fluid from the blood. When blood pressure is consistently high, it can damage the blood vessels in the kidneys and impair their ability to function correctly. This can lead to kidney disease or even kidney failure.
Heart failure is another potential complication of hypertension. As the heart muscles work harder to pump blood against high pressure, they can become weaker over time. This weakened heart muscle can eventually lead to heart failure, where the heart is unable to pump enough blood to meet the body’s needs.
Prevention and Management of Hypertension
Though hypertension is a chronic condition, it can be effectively managed through a combination of lifestyle changes and medication. Adopting a healthy lifestyle is the first line of defense against hypertension. This includes maintaining a balanced diet low in sodium and saturated fats, engaging in regular physical activity, maintaining a healthy weight, limiting alcohol consumption, and avoiding tobacco use.
In some cases, medication may be necessary to control blood pressure. There are various types of medications available, such as diuretics, beta-blockers, ACE inhibitors, and calcium channel blockers. These medications work by either reducing the volume of blood or relaxing and widening the blood vessels, effectively lowering blood pressure.
Regular check-ups with your healthcare provider are crucial for monitoring blood pressure levels and adjusting treatment plans if necessary. Your healthcare provider will assess your overall health, evaluate any risk factors, and determine the most suitable course of action to manage your hypertension effectively.

This image is property of pixabay.com.
The Importance of Early Detection
Early detection and timely intervention are vital in managing hypertension and reducing the risks of heart disease. Regular blood pressure screenings are essential for identifying high blood pressure in its early stages, even if you are not experiencing any noticeable symptoms. Detecting hypertension early allows for prompt intervention and lifestyle modifications to prevent further complications.
Addressing hypertension early on can significantly reduce the risk of developing heart disease. By managing blood pressure effectively, you can prevent the progression of arterial damage and reduce the strain on your heart. Maintaining healthy blood pressure levels minimizes the risk of heart attacks, strokes, and other cardiovascular events.
Reducing the Link between Hypertension and Heart Disease
To minimize the link between hypertension and heart disease, controlling blood pressure is of utmost importance. Consistently monitoring and managing blood pressure levels within the normal range significantly reduces the risk of complications. This can be achieved through a combination of lifestyle modifications and adherence to prescribed medication.
Reducing cardiovascular risk factors also plays a crucial role in preventing heart disease. This involves maintaining a healthy weight, managing diabetes and cholesterol levels, quitting smoking, and implementing stress management techniques.
Lastly, managing hypertension and preventing heart disease require life-long maintenance. It is essential to continue regular check-ups and screenings to ensure blood pressure remains within the target range. Additionally, sticking to a healthy lifestyle and prescribed treatments is necessary to control hypertension effectively and reduce the associated risks.
Research and Future Possibilities
Ongoing research is focused on developing new treatment approaches and identifying genetic factors that may contribute to hypertension. Advances in technology and medical understanding hold promising possibilities for improved management and prevention strategies.
New treatment approaches may aim to target specific mechanisms involved in hypertension and heart disease, allowing for more tailored and effective therapies. The identification of genetic factors may enable early risk assessment and personalized interventions to prevent the development of hypertension and its associated complications.
Public health strategies also play a significant role in addressing the global burden of hypertension. Education, awareness campaigns, and community interventions can help promote lifestyle modifications and encourage regular blood pressure screenings. Collaborative efforts between healthcare providers, researchers, and policymakers are essential in implementing effective public health initiatives.
Conclusion
Understanding the complex relationship between hypertension and heart disease is crucial for promoting heart health and preventing life-threatening complications. Hypertension, or high blood pressure, is a prevalent condition that significantly increases the risk of developing cardiovascular disease.
By recognizing the mechanisms behind the link, prioritizing prevention and management, and emphasizing early detection, individuals can take proactive steps to reduce the impact of hypertension on heart health. Adopting a healthy lifestyle, adhering to prescribed medication, attending regular check-ups, and staying informed about the latest research and developments are key in addressing hypertension and preventing heart disease.
Check out our Product Reviews